Supply Chain Resilience: Lessons Learned from Recent Disruptions

In the past few years, supply chains worldwide have faced unprecedented disruptions—from the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions to natural disasters and cyberattacks. These events exposed vulnerabilities in even the most sophisticated global supply chain networks, forcing companies to rethink their strategies for resilience.
As businesses strive to adapt, the question is no longer whether disruptions will occur, but how organizations can prepare, respond, and recover quickly when they do. This blog analyzes key lessons learned from recent crises and explores how companies can build more resilient supply chains, with a special focus on the transformative role of digital technologies like blockchain.
The New Reality: Why Supply Chain Resilience Matters
The global supply chain is a complex, interconnected web that delivers goods from raw materials to end consumers, but recent disruptions have exposed several critical challenges.
Many companies have struggled with a lack of transparency and visibility, making it difficult to trace products or components across multiple tiers of suppliers. An overreliance on single sources has left businesses vulnerable to localized shocks, while manual and siloed processes have slowed response times and hindered effective coordination among partners.
Additionally, compliance and fraud risks have increased, as crises can lead to a surge in counterfeit goods and regulatory breaches. These pain points highlight the urgent need for supply chains that are not only efficient, but also robust, adaptable, and transparent.
Lessons Learned from Recent Disruptions
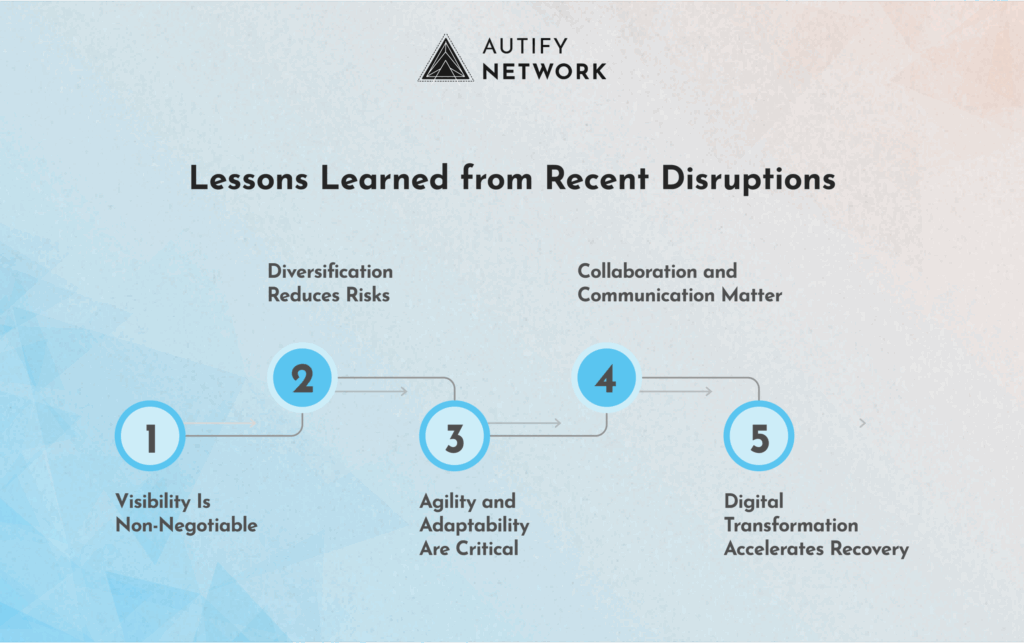
1. Visibility Is Non-Negotiable
One of the most important lessons is that end-to-end visibility is essential. Companies that had real-time insights into their inventory, suppliers, and logistics were able to react faster and make informed decisions. Those without such visibility faced delays, stockouts, and missed opportunities.
2. Diversification Reduces Risk
Relying on a single supplier, region, or logistics provider can be a recipe for disaster. Many organizations learned to diversify their supplier base, manufacturing locations, and transportation routes to spread risk and increase flexibility.
3. Agility and Adaptability Are Critical
Rigid supply chains struggled to pivot when faced with unexpected disruptions. Agile companies, on the other hand, could quickly reallocate resources, adjust production schedules, and find alternative suppliers.
4. Collaboration and Communication Matter
Strong relationships and open communication with suppliers, logistics partners, and customers proved invaluable. Companies that fostered collaboration were better equipped to share information, coordinate responses, and solve problems together.
5. Digital Transformation Accelerates Recovery
Firms that had invested in digital tools—such as cloud-based supply chain management, real-time analytics, and blockchain—were able to respond more effectively. Digitalization enabled automation, faster data sharing, and better scenario planning.
Strategies and Best Practices

1. Invest in End-to-End Visibility
Modern supply chains must be transparent at every stage, which involves implementing real-time tracking for shipments and inventory, mapping multi-tier supplier networks to identify vulnerabilities, and using dashboards and analytics to monitor performance and risks.
Blockchain technology is especially powerful in this context, as it provides an immutable, decentralized ledger that records every transaction and movement of goods. By enabling all stakeholders to access a single source of truth, blockchain significantly improves traceability and accountability across the entire supply chain.
2. Embrace Supplier and Geographic Diversification
To mitigate the risk of localized disruptions, companies should develop a diversified supplier portfolio that spans multiple regions and countries, qualify backup suppliers and logistics partners, and regularly assess the resilience of their most critical suppliers.
Diversification not only reduces vulnerability to unexpected shocks but also enhances a company’s bargaining power and operational flexibility, enabling businesses to adapt more effectively to changing market conditions.
3. Build Agility Through Scenario Planning and Flexibility
Resilient supply chains are designed to adapt to changing circumstances. Companies can achieve this by using scenario planning to anticipate potential disruptions and develop effective contingency plans, investing in flexible manufacturing and logistics capabilities, and enabling rapid reconfiguration of supply chain networks as conditions evolve.
Additionally, digital twins and simulation tools play a crucial role by allowing organizations to model different scenarios and test their response strategies, ensuring they are prepared for a wide range of challenges.
4. Strengthen Collaboration and Information Sharing
Breaking down silos and fostering collaboration is crucial for building effective supply chains. Best practices include establishing regular communication channels with key suppliers and partners, sharing forecasts, demand signals, and inventory data, and collaborating on risk assessments and joint response plans.
Blockchain platforms can further enhance these efforts by facilitating secure, transparent data sharing among authorized parties, which helps reduce disputes and delays while promoting greater trust and coordination across the supply chain.
5. Leverage Automation and Smart Contracts
Automation streamlines processes and reduces human error, and smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded on the blockchain—play a key role in this transformation.
They can automate payments upon delivery confirmation, enforce compliance with contractual terms, and reduce reliance on intermediaries, thereby speeding up transactions.
This approach not only increases efficiency but also minimizes the risk of fraud and disputes, creating a more reliable and transparent supply chain ecosystem.
6. Prioritize Compliance, Security, and Ethical Sourcing
Disruptions often increase the risk of regulatory breaches and unethical practices, making it essential for companies to safeguard their supply chains. By using blockchain to create tamper-proof records of compliance, certifications, and audits, organizations can ensure greater transparency and accountability.
Monitoring suppliers for adherence to environmental and social standards, as well as verifying product claims such as “organic” or “fair trade,” further strengthens the integrity of the supply chain. This approach not only helps prevent misconduct but also builds trust with customers, partners, and regulators.
7. Enable Real-Time Risk Management
Proactive risk management is key to building resilient supply chains. Companies should deploy real-time monitoring tools to quickly detect and address bottlenecks or quality issues, use predictive analytics to anticipate disruptions and optimize inventory levels, and establish rapid response teams for effective crisis management.
Blockchain’s real-time, immutable recordkeeping further supports swift identification and resolution of issues, making it easier to trace the root cause of problems and recover quickly from disruptions.
The Transformative Role of Blockchain in Supply Chain Resilience
Blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer for supply chain resilience by directly addressing core industry challenges. It creates a decentralized, tamper-proof record of every transaction, shipment, and handoff, ensuring all stakeholders can verify the origin, journey, and condition of goods while minimizing counterfeit products and fraud and streamlining compliance and audit processes.
With blockchain, companies gain real-time visibility into inventory, production, and logistics, while smart contracts automate essential processes such as payment releases upon delivery, compliance checks, certifications, and inventory replenishment.
Enhanced security is another key benefit, as decentralized data storage reduces the risk of single points of failure, cyberattacks, and data breaches, while ensuring data integrity and enabling secure sharing of sensitive information among partners.
Blockchain also streamlines supplier and vendor management by enabling secure, transparent verification and performance tracking, automating onboarding and compliance checks, and facilitating real-time monitoring of supplier performance to build stronger partnerships.
Furthermore, by supporting decentralized manufacturing networks, blockchain reduces reliance on centralized facilities, allowing production to continue even if one node is disrupted and fostering innovation through the secure sharing of intellectual property and designs.
Future Outlook: Innovations on the Horizon
As blockchain technology matures, its applications in supply chain resilience will continue to expand:
- Integration with IoT and AI: Combining blockchain with IoT sensors and AI analytics will enable even greater real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making.
- Decentralized autonomous supply networks: Blockchain-based platforms could enable fully decentralized, self-organizing supply chains that adapt dynamically to disruptions.
- Sustainability and ESG tracking: Blockchain will play a key role in verifying environmental and social claims, supporting circular economy initiatives, and enabling transparent carbon credit trading.
Companies that invest in these innovations will be better positioned to navigate future disruptions and seize new opportunities.
Conclusion
Recent disruptions have made it clear: resilience is the new competitive advantage in supply chain management. Companies must move beyond efficiency and embrace strategies that prioritize visibility, diversification, agility, collaboration, and digital transformation. Blockchain technology stands out as a powerful enabler, offering transparency, automation, security, and real-time risk management.
By learning from recent crises and leveraging advanced technologies, organizations can build supply chains that not only withstand shocks but also thrive in an unpredictable world. The future belongs to those who are prepared, adaptable, and committed to continuous innovation.